Spring Boot 配置文件深度解析
本文深入探讨了 Spring Boot 配置文件的核心作用及其主流格式。通过对比 Properties 与 YAML (YML) 的语法差异、优先级及适用场景,结合 @Value 与 @ConfigurationProperties 注解的代码实战,帮助开发者掌握配置读取的高级技巧。文章最后通过一个“图形验证码”综合案例,演示了如何将配置项优雅地集成到实际业务中。
Spring Boot 配置文件深度解析:从基础语法到验证码实战

摘要
本文深入探讨了 Spring Boot 配置文件的核心作用及其主流格式。通过对比 Properties 与 YAML (YML) 的语法差异、优先级及适用场景,结合 @Value 与 @ConfigurationProperties 注解的代码实战,帮助开发者掌握配置读取的高级技巧。文章最后通过一个“图形验证码”综合案例,演示了如何将配置项优雅地集成到实际业务中。
目录
1. 配置文件概述:告别硬编码
在软件开发中,硬编码 (Hard Coding) 是指将数据直接嵌入源代码的行为 。这种做法会导致程序灵活性差,例如手机字体大小若被写死,将无法满足不同用户的偏好 。
配置文件的作用在于解决硬编码问题,将易变信息(如数据库连接、端口号、第三方密钥)集中管理 。当程序启动时,它会从配置文件中读取数据并加载运行,从而实现用户与应用的交互 。
2. Spring Boot 配置文件的三大格式
Spring Boot 在启动时会自动从 classpath 路径寻找并加载以下格式的文件 :
| 格式名称 | 后缀名 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| Properties | .properties |
早期默认格式,创建项目时的默认选择 |
| YAML | .yml |
缩写形式,开发中最常用,支持树形结构 |
| YAML | .yaml |
全称形式,与 .yml 使用方式一致 |
2.1 优先级与共存说明
-
共存性:理论上两者可并存于同一项目 。
-
优先级:当配置冲突时,
.properties的优先级高于.yml。 -
建议:实际开发中应统一使用一种格式以降低维护成本 。
3. Properties 语法与读取实战
3.1 基础语法
Properties 采用 key=value 的键值对形式,使用 # 作为注释 。
文件配置如下:
# 设置项目启动端口
server.port=8080
# 数据库连接配置
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/testdb
spring.datasource.username=root
3.2 使用 @Value 读取配置
在 Java 代码中,可以使用 ${} ({}里面填写键名)格式配合 @Value 注解主动读取内容 。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequestMapping("/prop")
@RestController
public class PropertiesController {
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String url;
@RequestMapping("/read")
public String readProperties() {
return "从配置文件中读取url" + url;
}
}
运行效果: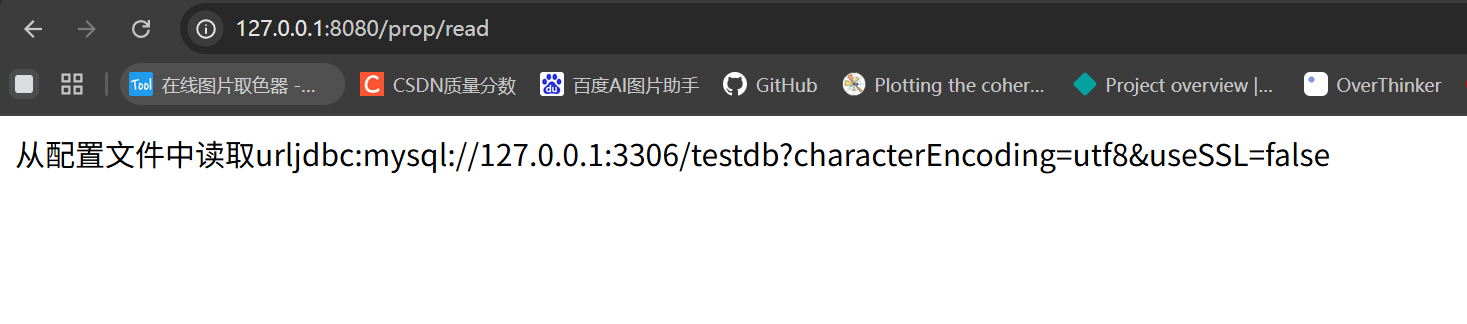
3.3 properties缺点
properties配置是以key-value的形式配置的,如下图所示: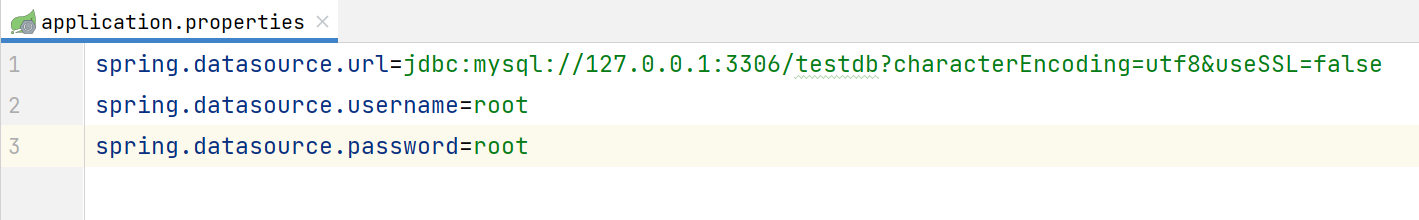
从上述配置key看出,properties配置文件中会有很多的冗余的信息,比如这些: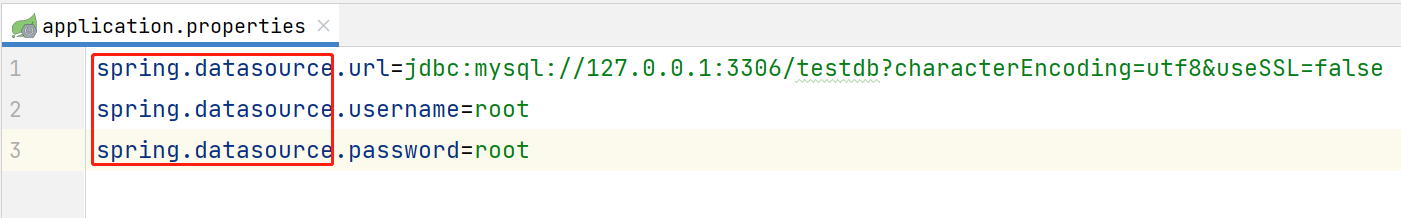
想要解决这个问题,就得使用yml配置文件的格式化了
4. YAML (YML) 进阶指南
YAML 是一种树形结构的标记语言,通过缩进表示层级 。
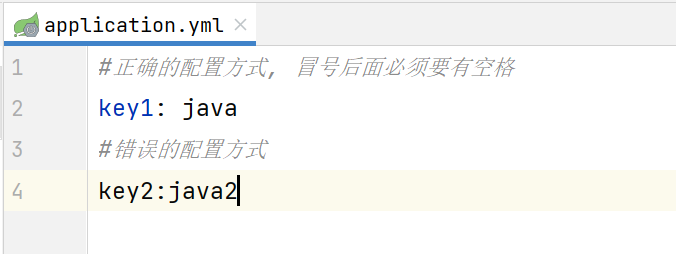
4.1 核心语法规范
-
冒号空格:
key和value之间必须有 英文冒号+空格,空格不可省略 。 -
数据类型支持:支持字符串、布尔值、整数、浮点数以及
null(用~表示) 。
单层级与多层级的表示规则
多层级的key前面要空两个格,且同级需对齐!
4.2 yaml语法与读取示例
yaml文件配置如下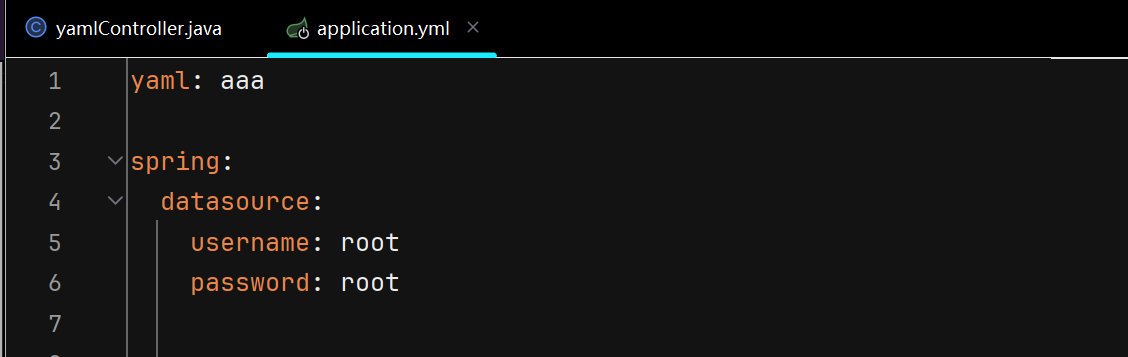
Java代码读取配置信息
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequestMapping("/yaml")
@RestController
public class yamlController {
@Value("${yaml}")
private String yaml;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String password;
@RequestMapping("/read")
public String read() {
System.out.println(yaml);
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
return "success";
}
}
运行结果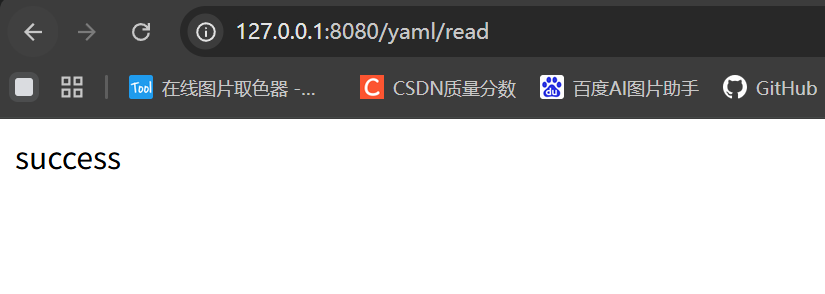
打印配置
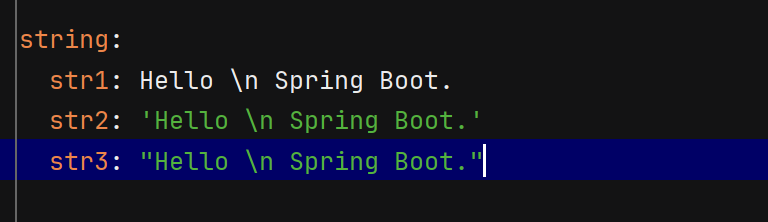
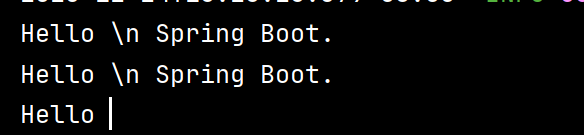
4.3 字符串的引号差异
YAML 中字符串默认不加引号,但单双引号有本质区别 :
-
单引号 (‘’):会转义特殊字符,使其变为普通字符串(如
\n输出为字符\n) -
双引号 (“”):不会转义特殊字符,保留其本身含义(如
\n输出为换行)
4.4 对象、集合与 Map 的读取
配置对象
YML 配置示例:
student:
id: 1
name: Java
age: 18
Java 实体类映射:
对于复杂数据形态,建议使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解 。
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") // 会从配置文件中找到student的前缀
@Configuration
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
运行打印结果
配置集合
YML 配置示例:
dbtypes:
name:
- mysql
- sqlserver
- db2
map:
k1: kk1
k2: kk2
k3: kk3
Java 实体类映射:
对于复杂数据形态,建议使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解 。
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dbtypes")
@Configuration
public class DbTypeConfig {
private List<String> name;
private Map<String, String> map;
}
运行打印结果
5. 综合性练习:验证码案例实战

本案例基于 Hutool 第三方工具包实现一个后端生成、校验验证码的功能 。
5.1 需求分析
-
后端生成验证码图片并返回流 。
-
将验证码及其生成时间存入
Session。 -
用户提交验证码,后端校验一致性及有效期(1分钟内有效) 。
5.2 约定前后端交互接口
接口定义
- 生成验证码
请求URL:/captcha/getCaptcha响应:验证码图片内容 - 校验验证码是否正确
请求:/captcha/check请求URL: /captcha/check 请求参数: captcha=xn8d响应:true
根据用户输⼊的验证码,校验验证码是否正确.true:验证成功.false:验证失败.
配置文件定义(解决硬编码问题)
在 application.yml 中定义验证码的尺寸及 Session 的 Key :
spring:
application:
name: spring-captcha-demo
captcha:
width: 100
height: 40
# 通过设置session配置项,避免日后需要到处修改
session:
code: SESSION_CODE_KEY
date: SESSION_DATE_KEY
验证码相关接口
import cn.hutool.captcha.CaptchaUtil;
import cn.hutool.captcha.LineCaptcha;
import cn.overthinker.spring.captcha.demo.model.CaptchaProperties;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.io.IOException;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/captcha")
public class CaptchaController {
@Autowired
private CaptchaProperties captchaProperties;
private static long VILD_MiLLTS_TIME = 5 * 60 * 1000;
@RequestMapping("/getCaptcha")
public void genCaptcha(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
//定义图形验证码的长和宽
LineCaptcha lineCaptcha = CaptchaUtil.createLineCaptcha(captchaProperties.getWidth(), captchaProperties.getHeight());
String code = lineCaptcha.getCode();
System.out.println(code);
//图形验证码写出,可以写出到文件,也可以写出到流
try {
response.setContentType("image/jpeg");
response.setHeader("Pragma", "No-cache");
lineCaptcha.write(response.getOutputStream());
//拿到这个请求的session,并且将code写入到session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.setAttribute(captchaProperties.getSession().getCode(), code);
//记录时间保持五分钟内有效
session.setAttribute(captchaProperties.getSession().getDate(), System.currentTimeMillis());
response.getOutputStream().close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@RequestMapping("/check")
public Boolean checkCaptcha(String captcha, HttpSession session) {
//先判断是否为空
if(!StringUtils.hasLength(captcha)) {
return false;
}
// 从session中获取code和时间
String code = session.getAttribute(captchaProperties.getSession().getCode()).toString();
long data = (long)session.getAttribute(captchaProperties.getSession().getDate());
if(captcha.equalsIgnoreCase(code) && (System.currentTimeMillis() - data < VILD_MiLLTS_TIME)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
前端相关代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>验证码</title>
<style>
#inputCaptcha {
height: 30px;
vertical-align: middle;
}
#verificationCodeImg{
vertical-align: middle;
}
#checkCaptcha{
height: 40px;
width: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
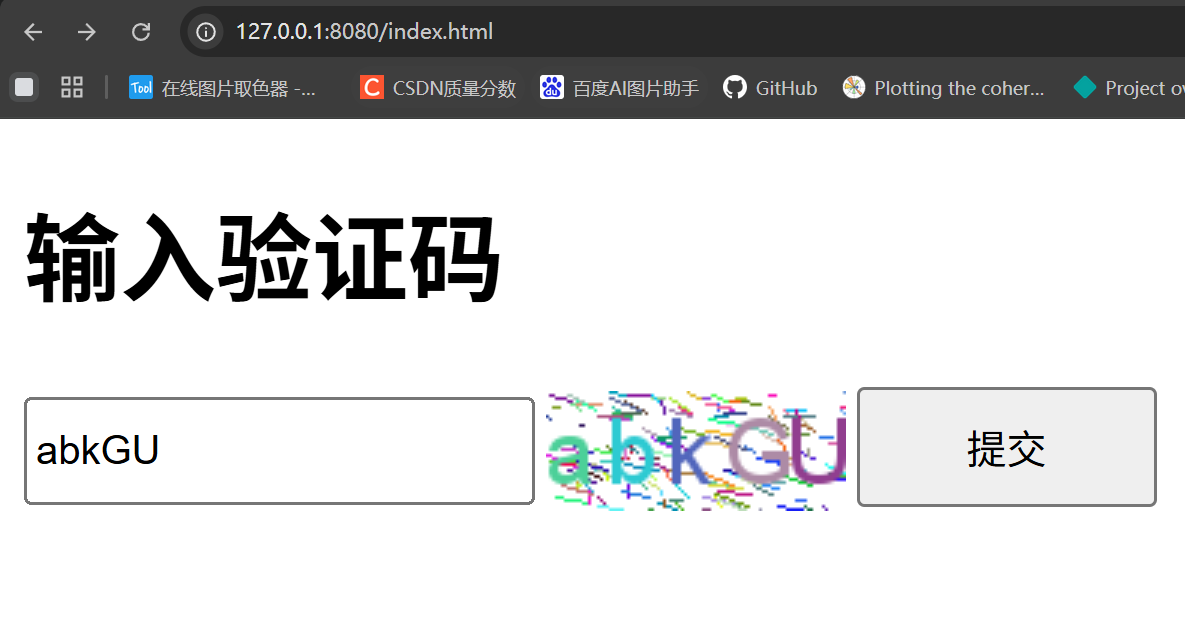
<h1>输入验证码</h1>
<div id="confirm">
<input type="text" name="inputCaptcha" id="inputCaptcha">
<img id="verificationCodeImg" src="/captcha/getCaptcha" style="cursor: pointer;" title="看不清?换一张" />
<input type="button" value="提交" id="checkCaptcha">
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.4/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
$("#verificationCodeImg").click(function(){
$(this).hide().attr('src', '/captcha/getCaptcha?dt=' + new Date().getTime()).fadeIn();
});
$("#checkCaptcha").click(function () {
// alert("验证码校验");
$.ajax({
url:'/captcha/check',
type:'post',
data:{
captcha:$('#inputCaptcha').val()
},
success:function (result) {
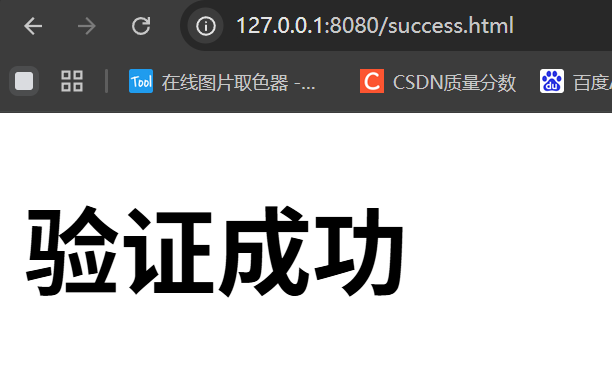
if(result){
location.href = 'success.html';
}else {
alert("验证码错误!");
}
}
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
运行结果
6. 总结
-
Properties 语法简单但存在冗余,适用于简单项目 。
-
YAML 结构清晰、支持类型丰富,是目前 Spring Boot 开发的主流选择 。
-
读取技巧:简单配置用
@Value,结构化配置(对象/集合)首选@ConfigurationProperties。 -
建议:yml可以和properties共存,但⼀个项目中建议只使用⼀种配置类型文件
参考链接:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容











所有评论(0)