Vue 响应式原理简易实现
在Vue框架中vue能够做到数据变化时视图自动更新,主要依靠其响应式方式,今天我分享便是它的简易实现。
Vue 响应式原理简易实现
在Vue框架中vue能够做到数据变化时视图自动更新,主要依靠其响应式方式,今天我分享便是它的简易实现。
一、Vue 实例的构造与初始化
基础结构:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="./index.js"></script>
<div id="app">
<h1>标题是:{{ myTitle }} -- {{ myTitle }}</h1>
<p>内容是: {{ myContent }} </p>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
myTitle:'这是一个标题',
myContent:'这是一段文本'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
预览: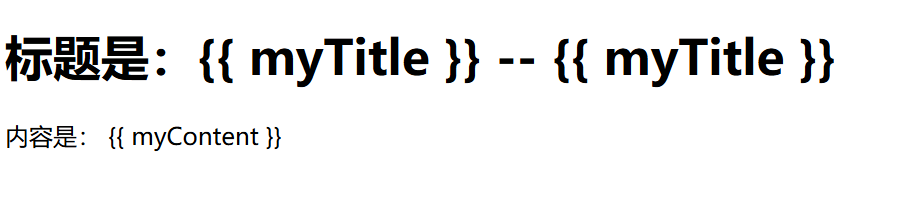
(一)Vue 类的构造函数
首先看 Vue 类的构造函数:
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
this.$options = options || {};
this.$data = options.data || {};
const el = options.el;
this.$el = typeof el === 'string' ? document.querySelector(el) : el;
// 1. 将 data 中的属性代理到 Vue 实例上
proxy(this, this.$data);
// 2. 对 data 进行响应式观测
new Observer(this.$data);
// 3. 解析模板,建立数据与视图的关联
new Compile(this);
}
}
当我们 new 一个 Vue 实例时,会依次做三件关键事:
- 属性代理:通过
proxy函数,把data对象里的属性“代理”到 Vue 实例上,这样我们可以直接用this.xxx访问data.xxx。 - 响应式观测:创建
Observer实例,对data进行递归的响应式处理,让data里的每个属性都具备“被监听”的能力。 - 模板解析:创建
Compile实例,解析页面中的模板(比如包含{{}}插值的节点),建立数据和 DOM 之间的关联。
(二)proxy:让属性访问更便捷
proxy 函数的作用是属性代理:
function proxy(target, data) {
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(target, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
return data[key];
},
set(newValue) {
data[key] = newValue;
}
})
})
}
举个例子,如果 data 里有 name: 'Vue',原本要通过 this.$data.name 访问,经过代理后,直接 this.name 就能拿到值,赋值时 this.name = 'React' 也会同步修改 data.name。这一步是为了让开发者用起来更顺手,隐藏了 $data 这个中间层。
二、Observer:让数据变得“可观测”
(一)Observer 类的职责
Observer 类负责把普通的 data 对象变成“响应式”对象:
class Observer {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.dep = new Dep();
this.walk(data)
}
walk(data) {
const dep = this.dep;
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => defineReactive(data, key, data[key], dep))
}
}
它的核心是 walk 方法,遍历 data 中的每个属性,然后调用 defineReactive 函数,对每个属性进行“响应式化”处理。
(二)defineReactive:给属性加“监听器”
defineReactive 是响应式的核心实现:
function defineReactive(data, key, value, dep) {
if (typeof value === 'object' && value !== null) {
return new Observer(value);
}
Object.defineProperty(data, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
Dep.target && dep.addSub(Dep.target);
return value;
},
set(newValue) {
if (value === newValue) return;
value = newValue;
if (typeof value === 'object' && value !== null) {
return new Observer(value);
}
dep.notify(); // 通知更新
}
})
}
- get 方法:当属性被访问时(比如模板里用到
{{name}},读取name时),如果存在Dep.target(后面会讲,这是Watcher实例),就把这个Watcher加入到当前属性的依赖集合dep中,这一步叫“依赖收集”。 - set 方法:当属性被赋值时,先判断新值和旧值是否一样,不一样的话更新值。如果新值是对象,还需要递归地把新对象也变成响应式。最后,通过
dep.notify()通知所有依赖这个属性的Watcher,让它们去更新视图。 - Dep 类:
Dep是“依赖收集器”,每个响应式属性都有一个对应的Dep实例,用来存储依赖它的Watcher:class Dep { constructor() { this.subs = [] } addSub(sub) { this.subs.push(sub); } notify() { this.subs.forEach(sub => sub.update()); } }
三、Watcher:数据与视图的“纽带”
(一)Watcher 类的作用
Watcher 是连接数据和视图的桥梁:
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, callback){
this.vm = vm;
this.key = key;
this.callback = callback;
Dep.target = this;
this.oldValue = vm[key];
Dep.target = null;
}
update(){
const newValue = this.vm[this.key];
if(this.oldValue === newValue) return;
this.callback(newValue);
this.oldValue = newValue;
}
}
当创建 Watcher 实例时,会先把 Dep.target 指向自己,然后访问 vm[key](触发属性的 get 方法),这样 get 方法里的 dep.addSub(Dep.target) 就会把当前 Watcher 加入到属性的依赖集合中。之后,Dep.target 重置为 null,避免后续无关的依赖收集。
当数据变化时,Dep 会调用 Watcher 的 update 方法,update 里会拿到新值,和旧值比较,如果不一样,就调用回调函数去更新视图。
四、Compile:解析模板,建立关联
(一)Compile 类的工作
Compile 类负责解析模板,找到数据和 DOM 的关联,并创建 Watcher 来监听数据变化:
class Compile {
constructor(vm){
this.vm = vm;
this.el = vm.$el;
this.compile(this.el);
}
compile(el) {
const childNodes = el.childNodes;
Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node=>{
//1 表示元素节点,就是 HTML 里的各种标签,比如 div、p、span 这些。
//2 表示属性节点,指的是元素的属性,比如 class、id
//3 表示文本节点,就是元素里的文字内容,比如<p>里面的文字。
if(node.nodeType === 3){
this.compileText(node); // 文本节点
}else if(node.nodeType === 1){
// 元素节点(可扩展处理指令等,这里暂略)
}
if(node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length !== 0){
this.compile(node);
}
})
}
compileText(node) {
const reg = /\{\{(.+?)\}\}/g;
const value = node.textContent.replace(/\s/g,'');
const tokens = [];
let result, index, lastIndex = 0;
while(result = reg.exec(value)){
index = result.index;
if(index > lastIndex){
tokens.push(value.slice(lastIndex, index));
}
const key = result[1].trim();
tokens.push(this.vm[key]);
lastIndex = index + result[0].length;
const pos = tokens.length - 1;
// 创建 Watcher,数据变化时更新节点文本
new Watcher(this.vm, key, newValue => {
tokens[pos] = newValue;
node.textContent = tokens.join('');
});
}
if(lastIndex < value.length){
tokens.push(value.slice(lastIndex));
}
if(tokens.length){
node.textContent = tokens.join('');
}
}
}
nodeType的几种常见情况:
result = reg.exec(value)的输出结果:
compile 方法递归遍历 DOM 节点,遇到文本节点时,调用 compileText方法。compileText 会用正则匹配 {{}} 格式的插值表达式,提取出数据的 key,然后创建 Watcher 监听这个 key 对应的数据变化。当数据变化时,Watcher 的回调函数会更新节点的文本内容。
五、整体过程
-
初始化阶段:
- 构造
Vue实例,进行属性代理、响应式观测、模板解析。 Observer遍历data,通过defineReactive给每个属性加上get/set拦截,同时为每个属性创建Dep。Compile解析模板,遇到插值表达式,提取数据key,并为每个key创建Watcher,Watcher触发get方法,完成“依赖收集”(把自己加入Dep)。
- 构造
-
数据更新阶段:
- 当我们修改数据(如
this.name = 'New Name'),会触发属性的set方法。 set方法里调用dep.notify(),通知所有依赖该属性的Watcher。Watcher的update方法被调用,执行回调函数,更新对应的 DOM 节点,视图随之更新。
- 当我们修改数据(如
预览:

出处详见:vue2响应式系统
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容







所有评论(0)